SSL processing in Java based application services might produce a significant overhead to service latency. Deciding which SSL termination setup to use in terms of performance can be a daunting task.
In this paper, we will evaluate the performance of different SSL termination setups in Java-based application services. For each approach, we will describe the SSL termination setup and present performance measurements. Finally, we will compare the different approaches by analysing the measurement results.
For our specific use-case, we will be evaluating an HTTP service implemented with embedded Jetty and simple Java servlets.
Below is a detailed description of performance setup
Application setup
- Application service instances: 2
- Processor: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2686 v4 @ 2.30GHz
- CPUs/instance: 4
- Memory/instance: 16 GB
Application Configuration
- Jetty thread pool (dynamic):
- Max threads: 200
- Min threads: 8
- Queue capacity: 200
- Graceful timeout: 60 seconds
Load Setup
- Load worker instances: 2
- Processor: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2686 v4 @ 2.30GHz
- CPUs/instance: 4
- Memory/instance: 16 GB
SSL Termination Setup
Since major suspect of high latency was SSL overhead, load was conducted with three different SSL termination setups:
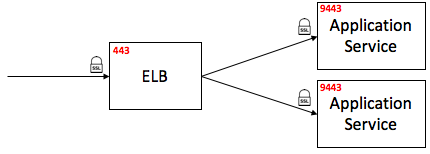
1) Application Service (Jetty) SSL Processing: In this setup, SSL termination was done by application’s Jetty server.
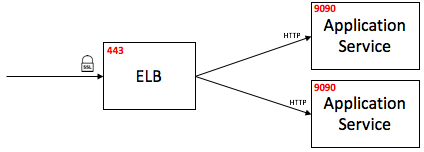
2) ELB SSL Termination: In this setup, TLS was disabled in application service and moved to ELB end. Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) is a load-balancing service by Amazon Web Services (AWS). Server certificates were installed on ELB and SSL termination was done by ELB.
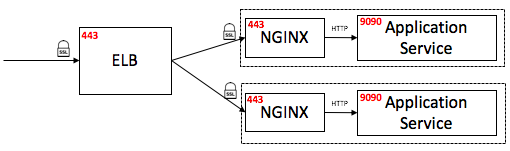
3) Nginx Proxy SSL Termination: In this setup, An Nginx reverse proxy server was installed in each application service machine, facing the ELB. Nginx was responsible for the SSL termination and forwarded traffic internally to application service (localhost:9090).
Summary
- SSL termination on Amazon ELB produced best measurements, performance-wise.
- With TLS enabled, CPU has reached nearly full usage at ~55 concurrent users only. Same CPU usage was reached with ELB after > 3500 concurrent users.
- NGINX performed very well under minor load, but started to deteriorate during medium load.
- NGINX produced highest standard deviation values for response time.